Main Ingredients
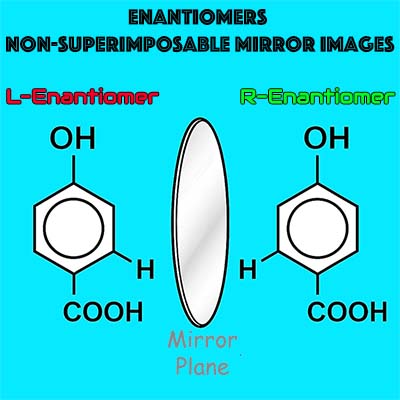
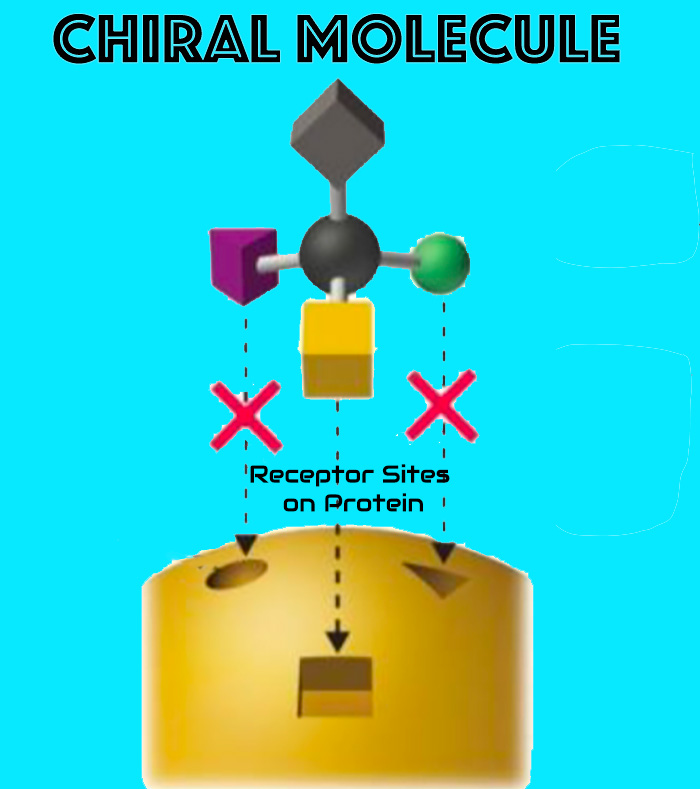
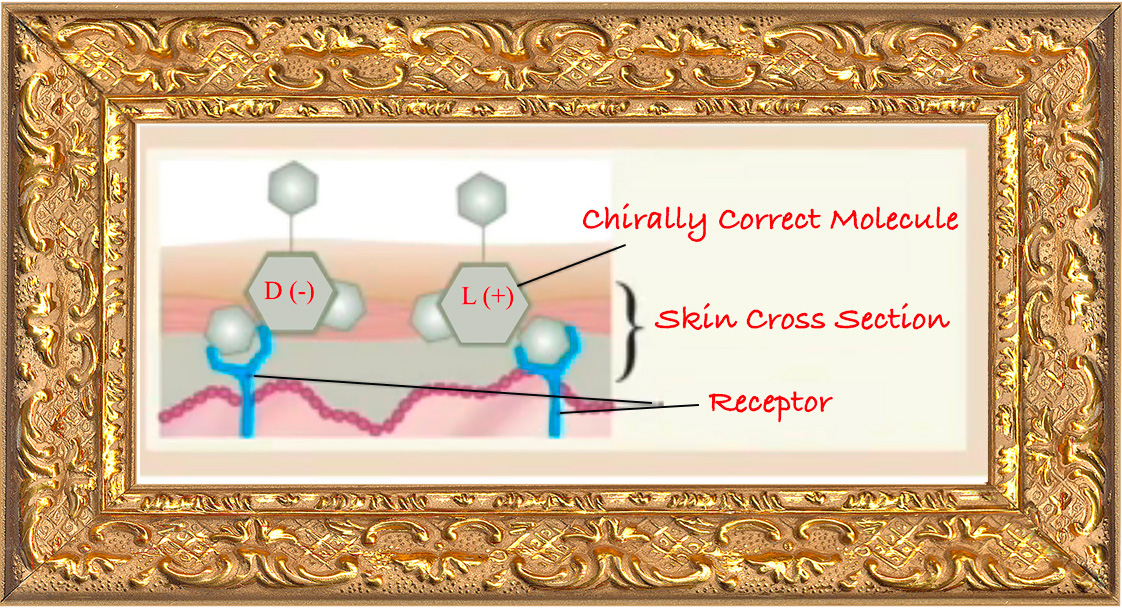
The active component is a single, stereochemically pure enantiomer of an aromatic acid, produced under strict enantiomeric controls to ensure consistent clinical performance and tissue compatibility.
- Identity: chiral aromatic acid (single enantiomer, non-racemic)
- Purity: enantiomeric excess (ee) ≥ 99% (lot-dependent, QC-verified)
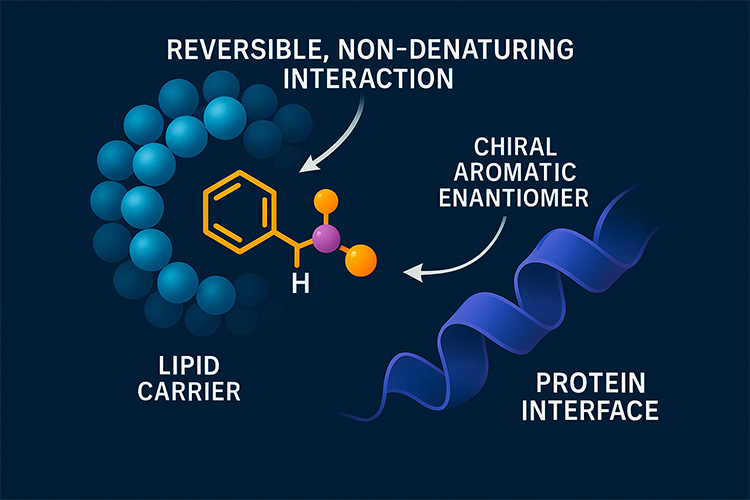
- Function: selective interactions at protein interfaces without necrosis
- Consistency: batch-to-batch reproducibility with validated chiral analytics
Physicochemical properties
| Chirality | Single enantiomer (non-racemic) |
| Acid–base | Weak acid; pKa consistent with tissue tolerance |
| Lipophilicity | Balanced (see carrier synergy below) |
| Reactivity | Predictable, protein-selective interactions |
Mechanism (concise)
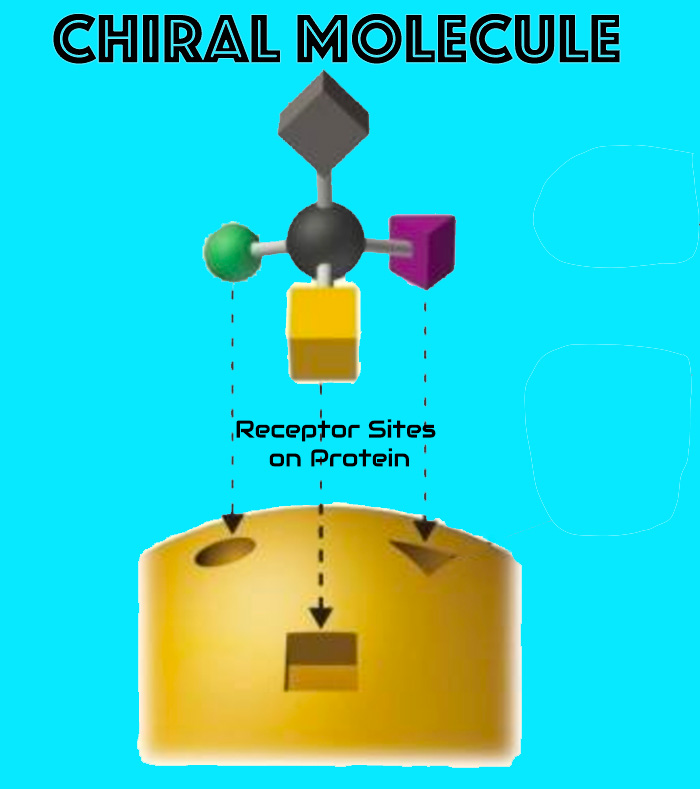
The enantiopure configuration promotes stereoselective, non-necrotic interactions with tissue proteins, supporting functional tissue remodeling while preserving viability.
- Chiral fit → improved selectivity
- Predictable local kinetics
- No coagulative necrosis pathway